Cyber security comes up in every conversation we have with business leaders throughout North America these days. Business leaders know that the increase in cyber attacks on small to mid-sized businesses is a genuine threat and that increasing cyber security measures is of the utmost importance.
One question we repeatedly hear during these discussions is: “What can I do to protect my business from cyber security threats”?
The answer isn't as simple as one tool or technology to stop all cyber threats. Rather, it's a combination of security layers that are designed to protect your business from many angles.
One of those critical layers is vulnerability scanning.
Regular internal and external vulnerability scans are valuable components of any business cyber security plan. However, vulnerability scans can be complicated and challenging to implement because few people know what they are or where to start. We're here to help.
In this article, we’ll discuss:
- What Is a Vulnerability Scan?
- Internal vs. External Vulnerability Scanning: What’s the Difference?
- What is External Vulnerability Scanning?
- What is Internal Vulnerability Scanning?
- Where to Start with Vulnerability Scanning
What Is a Vulnerability Scan?
Vulnerability scans help identify potential weaknesses in your network. The results of these scans allow you to prioritize and mitigate the weaknesses that are found before a cyber criminal can exploit them.
Internal vs. External Vulnerability Scanning: What’s the Difference?
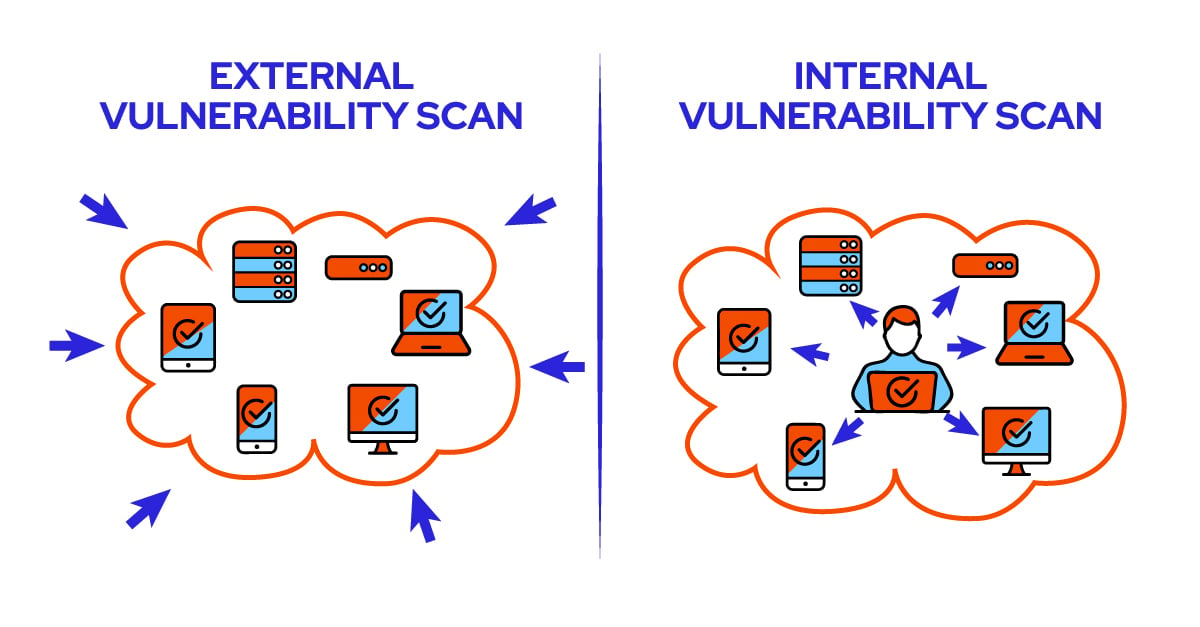
External vulnerability scanning looks for weaknesses from outside your network to provide you with the valuable info needed to protect your network from outside threats.
Internal vulnerability scans are performed from inside your network and provide a higher-level analysis of vulnerabilities such as outdated software and patches, along with checking all of your endpoints for possible weaknesses.
Let’s take a more in-depth look at internal and external vulnerability scanning.
What is External Vulnerability Scanning?
External vulnerability scans are performed from outside your network. They reveal externally-accessible weaknesses that could compromise your network. These scans target your company’s public IP addresses to give you insight into vulnerabilities that any hacker on the internet could target.
Benefits of an External Vulnerability Scan
External scans provide numerous benefits for vulnerability management.
- Be Proactive - By identifying weaknesses that might lead to cyber security incidents, external vulnerability scans help your organization take a proactive approach by upgrading out-of-date services and correcting misconfigurations such as unnecessary open ports.
- Prioritize - External scans also help you prioritize your efforts by pinpointing the most pressing issues on your network from an outside viewpoint. They help with verifying the proper configuration and maintenance of your business’s externally facing services easier.
- Easily Identify Changes - With regular external vulnerability scanning, it’s easier to identify any new servers or services implemented since you performed your last scan. The scan will tell you whether these devices or services bring any new risk to your network.
Some of the known vulnerabilities that an external scan can help you identify include:
- Vulnerable software versions, including out-of-date web hosting software with known vulnerabilities such as the recent Log4j exploit.
- Weaknesses in the encryption configuration of your services, such as allowing deprecated ciphers/protocols like TLS 1.0 or SSL3.
- Misconfigured services, like leaving RDP ports open to the internet.
How Often Should You Perform External Vulnerability Scans?
At a minimum, external vulnerability scans should happen once per quarter. However, depending on your unique organizational needs, you may end up performing scans monthly or even weekly.
The quarterly period often strikes a balance between not scanning your network enough, potentially missing significant configuration changes -- and scanning it too much, generating similar reports that wind up ignored as noise.
As you scan your network for external threats, it’s best to pay attention to any new servers or services that come up. These changes can be used to back-check your formal change-control process, catching any new systems that may not have gotten proper security consideration and screening before being implemented.
What is Internal Vulnerability Scanning?
Internal vulnerability scans are performed from inside the network you’re scanning. Since these scans run from an already privileged position, an internal vulnerability scan can show vulnerabilities at much greater depth than you’d see with an external scan.
Internal scans can verify that patching has occurred and provides detailed reports on vulnerabilities within all the endpoints on your corporate network – not just those accessible from the internet.
Benefits of an Internal Vulnerability Scan
Several benefits come from performing an internal vulnerability scan.
For starters, all the benefits of an external scan – locating out-of-date and vulnerable software versions, weak encryption, and misconfigured services – are applied to all endpoints on your network. These insights, when acted upon, can significantly increase your organization’s resistance to cyber attacks from threats that manage to get past your firewall.
It also demonstrates your organization’s proactive approach to cyber security and can provide you with better cyber insurance coverage and premiums.
When analyzing data from an internal vulnerability scan, the trends you should pay attention to include missing patches and the top vulnerable machines in your network.
Similarly, common vulnerabilities to keep in mind include:
- End-of-life operating systems that no longer receive security updates, such as Windows 7.
- Known vulnerabilities with exploits in the wild, including EternalBlue, Heartbleed, and DROWN.
- Third-party software on your network is in need of security patches, especially web browsers.
How Often Should You Perform Internal Vulnerability Scans?
There’s no specific answer to this question because it all depends on the industry you're in and the type of business you conduct. For example, if your business is in the DOD supply chain, you may need to perform vulnerability assessments more frequently than a company that doesn’t need to worry about CMMC compliance.
Ideally, as with external scans, you should run a scan at least once per quarter. Staying on top of your vulnerabilities enables you to patch them early before hackers can take advantage.
Where to Start with Vulnerability Scans
The primary objective of internal and external vulnerability scans is to identify servers, systems, and software with known security vulnerabilities so that you can take action to improve their security before weaknesses are exploited.
That is vulnerability management.
That said, here are key considerations to keep in mind when undertaking a vulnerability scan:
1. Define the Scope
Before you get started on an internal or external vulnerability scan, have an idea of what you’re scanning in the first place.
At a minimum, you will need to know your external IP addresses to perform an external vulnerability scan. You also will need to know the IP ranges of your internal network to conduct an internal scan.
2. Asset Management
Your organization should maintain a database of the systems and networks under the IT department’s management. Likewise, you should keep track of the digital assets your business is responsible for – customer data, commonly used software, etc.
Knowing these things will help you act on the information provided by vulnerability scans.
For instance, when an old database is flagged as exploitable by a vulnerability scan, you will be able to turn it off or isolate it without having to figure out what it does because you will already know. As existing systems change their domains and IP addresses, keeping your documentation up-to-date ensures that nothing falls through the gaps when performing vulnerability scans.
3. Scoping Strategies
Once you know what assets you have, how do you pinpoint what to scan?
Businesses use different types of systems and services, from local workstations and servers to cloud systems from providers like Google Cloud, AWS, and Azure. Deciding what needs to get scanned can be challenging, but once you know what assets you have, you can categorize and prioritize them based on their security needs.
The main categories to consider are exposure and sensitivity.
Systems that are publicly accessible over the internet are the most exposed as they are susceptible to attacks 24/7. Therefore, external vulnerability scans should be your first priority if you are responsible for any publicly accessible services.
For internal assets, priority should be given to servers and subnets with your most valuable and sensitive information. Even the data stored in a backup and protected from the internet by a firewall can still be vulnerable to malware that gets onto your internal network through email or a USB drive.
Internal vulnerability scans help you to safeguard your assets against such possible attacks.
Ready to Take Vulnerability Management to the Next Level With Vulnerability Scanning?
Vulnerability management is a valuable component of running a secure business of any size, and it starts with regular vulnerability scans.
With companies facing an increasing and ever-present threat from cyber attacks, external and internal vulnerability scans can help you discover weaknesses, minimize risk, and prevent cybersecurity incidents.
If you’re looking for a cyber security services company in North America that can provide a convenient and scalable vulnerability scanning solution, give us a call. As part of our managed cyber security services, we'll identify security weaknesses in your digital environment and reduce your cyber exposure.


